What Is ‘Human Risk’ in Cyber?
May 22

Experience OutThink
Let’s be honest: when we think of cybersecurity threats, we imagine hoodie wearing hackers tapping away in a dark room. And that's true, yet it doesn't capture the full reality.
What if the real risk was sitting at your desk, sipping coffee, and clicking on that “urgent” email from the so-called IT department? This is the uncomfortable truth about cybersecurity: human beings become the vulnerability, and that’s what’s meant by human risk.
So, What Exactly Is “Human Risk”?
Human risk is your biggest security blindspot: the moment when someone makes a split second decision that compromises your security infrastructure. It refers to the potential for people, employees, vendors, or even customers, to unintentionally compromise an organization’s cybersecurity. This includes falling for phishing scams, using weak passwords, sharing sensitive data, or just being plain careless.
Sounds simple, right? But here's the kicker: According to the Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, more than 74% of data breaches in 2023 were caused by human error and not by sophisticated malware or SQL injections!
The numbers don't lie.
Why Are Humans So Risk-Prone?
We as humans are often emotional, distracted, and multitasking. Cybercriminals know this! and they’re masters at exploiting our psyche.
Here are a few reasons why we make mistakes online:
- We trust too easily: A friendly looking email from your “CEO” asking for gift cards? That’s a classic phishing scam. But hey, it looked real.
- We love shortcuts: Saving passwords in browsers, using “123456” as a password or skipping those boring cybersecurity training - these are habits attackers count on.
- We get distracted: You’re rushing to meet a deadline, juggling emails, Slack messages, and Zoom calls. Boom! You clicked the wrong link accidentally.
When was the last time you paused a moment before you clicked on a link without thinking twice? If you can't remember, you're proving the point.
Types of ‘Human’ Cyber Risks
Let’s break it down the 3 main types of cybersecurity human risk:
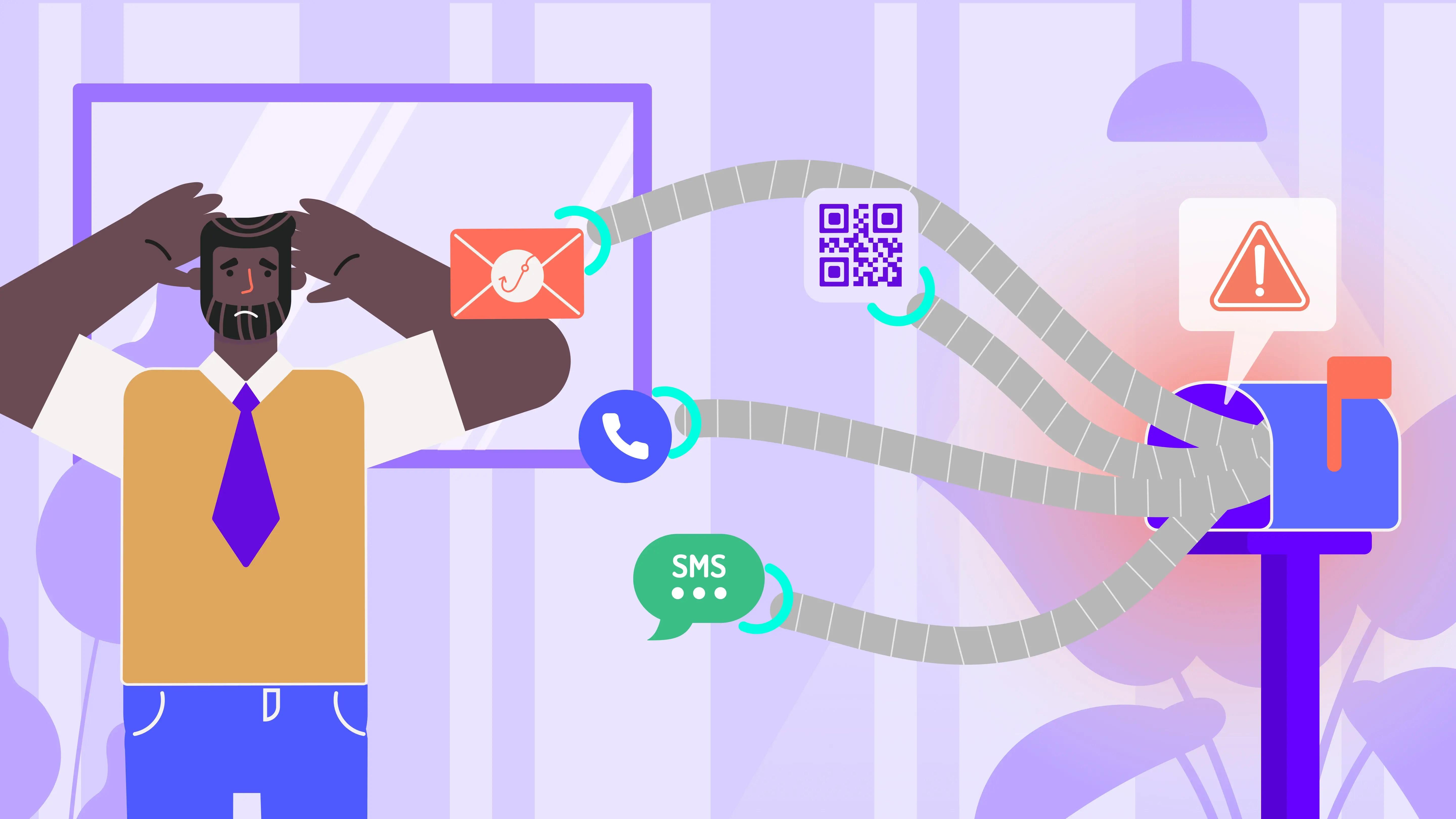
1. Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing remains the top way hackers get in. These emails or messages trick users into sharing credentials or downloading malware. Here's the kicker: 36% of all the data breaches involve phishing. Yes! And phishing accounts for 39.6% of all email threats, making it the most common email attack method.
And what’s the price you pay? According to IBM/Ponemon studies report 2024, phishing-related breaches cost companies on average $4.88 million annually. Every minute your team goes untrained, you're rolling the dice with a million-dollar breach.
2. Insider Threats
These are risks that come from people inside your organization. This could be a disgruntled employee leaking data or an unaware intern/employee uploading sensitive files to a public cloud service.
According to Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, 19% of breaches involved internal actors.
3. Poor Password Practices
Brace yourself for this: 65% of people reuse the same password across multiple accounts! Using the same password everywhere is like using the same key for your house, car, and office safe. That means if a hacker cracks one account, they can break into others like dominoes.
Why Human Risk Is Hard to Solve
You can install firewalls, anti-virus, and the fanciest security tools, but you can’t "install" secure behaviors into human beings. That requires time, education, investment, and the culture to nurture them.
The challenge with human risk is that it evolves. Today’s phishing scam is tomorrow’s deepfake voice message from your “boss.” As technology gets smarter and attackers get more sophisticated, training once a year just won’t cut it anymore.
So… What Can We Do About It?
Thankfully, there’s a growing focus on Cybersecurity Human Risk Management (HRM) in the security space. It’s not about blaming people, it’s about empowering them.
Here’s how organizations are tackling the problem:
1. Ongoing Cybersecurity Awareness Training
This isn’t your boring annual quiz anymore! Modern training includes interactive videos, phishing simulations, and even games. In a recent study, consistent security awareness training was proven to reduce employee phishing susceptibility by 60%.
But frequency matters! According to NIST, behavior-based, frequent training has a significantly higher impact than once-a-year refreshers.
This is exactly where OutThink comes in! Designed to make cybersecurity awareness both effective and engaging, OutThink turns training into real behavior change by delivering personalized, context-aware learning based on each user’s risk profile.
2. Behavioral Analytics
Think of this as cybersecurity with a bit of psychology. By analyzing how employees interact with systems, HRM tools can spot risky behaviors in seconds.
Gartner predicts that by 2026, 70% of large enterprises will use behavioral analytics to reduce insider threats.
3. Password Managers and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Encouraging (or forcing) employees to use password managers reduces the chance of password reuse. MFA adds a second layer of defense, even if a password is stolen, access isn't guaranteed.
The Future of Human Risk
As AI tools like ChatGPT get more advanced, phishing and scams will become even more personalized and convincing. Already, attackers are using AI to craft messages that sound just like your coworker or manager.
This means our human radar needs to be sharper and smarter.
The good news? With the right human risk management approach of awareness, culture, and smart tools, we can reduce human risk. After all, while people might be considered as the weakest link today, they can also become the strongest and best first line of defense.
Managing Human Risk in Cyber
Human risk in cybersecurity isn’t just a crack in the firewall, it’s the unlocked front door. The question today isn't whether human risk will impact your organization. It's whether you'll get ahead of it before it costs you millions.
And the key? It’s in you employees’ hands. But that’s also the opportunity! When you adopt a human risk management approach to train, empower, and support people, you create a resilient, human-first cybersecurity culture.
So next time an employee receives that email asking for “urgent help” or a surprise password reset, they’ll take a breath. They’ll think twice. They’ll report it.
And they’ll have prevented your company from being the next headline.