State-Sponsored Phishing Attacks Target 40,000 Corporate Users: What This Means for Protecting Your Business
Jul 18

Discover OutThink's AI-Powered Phishing Simulator
In a world where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, a new report uncovers a significant campaign of state-sponsored phishing attacks targeting approximately 40,000 corporate users worldwide. Leveraging advanced phishing tactics, these state-backed malicious actors are infiltrating corporate networks, posing serious risks to organizations across various sectors. This blog post breaks down the details of this threat, explains why it matters, and outlines how to protect your organization from such sophisticated, government-supported attacks.
The Scope of the State-Sponsored Phishing Attack
The recent cyber threat involves attackers believed to be backed by state-sponsored entities. These cybercriminals have set their sights on a vast number of corporate users, primarily through elaborate state-sponsored phishing campaigns. The scale of targeting 40,000 users underscores a well-coordinated effort with significant backing and resources, indicating that this campaign is not only well-financed but also strategically aligned to target vulnerable industries.
According to Menlo Security’s Global Cyber Gangs report, these state-sponsored actors have launched multiple Highly Evasive Adaptive Threat (HEAT) campaigns, specifically targeting C-suite executives in industries like banking, healthcare, and government. The report highlights how campaigns like LegalQloud, Eqooqp, and Boomer have successfully bypassed traditional security measures, illustrating how quickly state-sponsored phishing attackers adapt their tactics to outpace corporate defenses. This finding underscores the importance of strengthening defenses against state-sponsored phishing efforts, as standard security measures may not suffice.
Phishing Tactics at Play
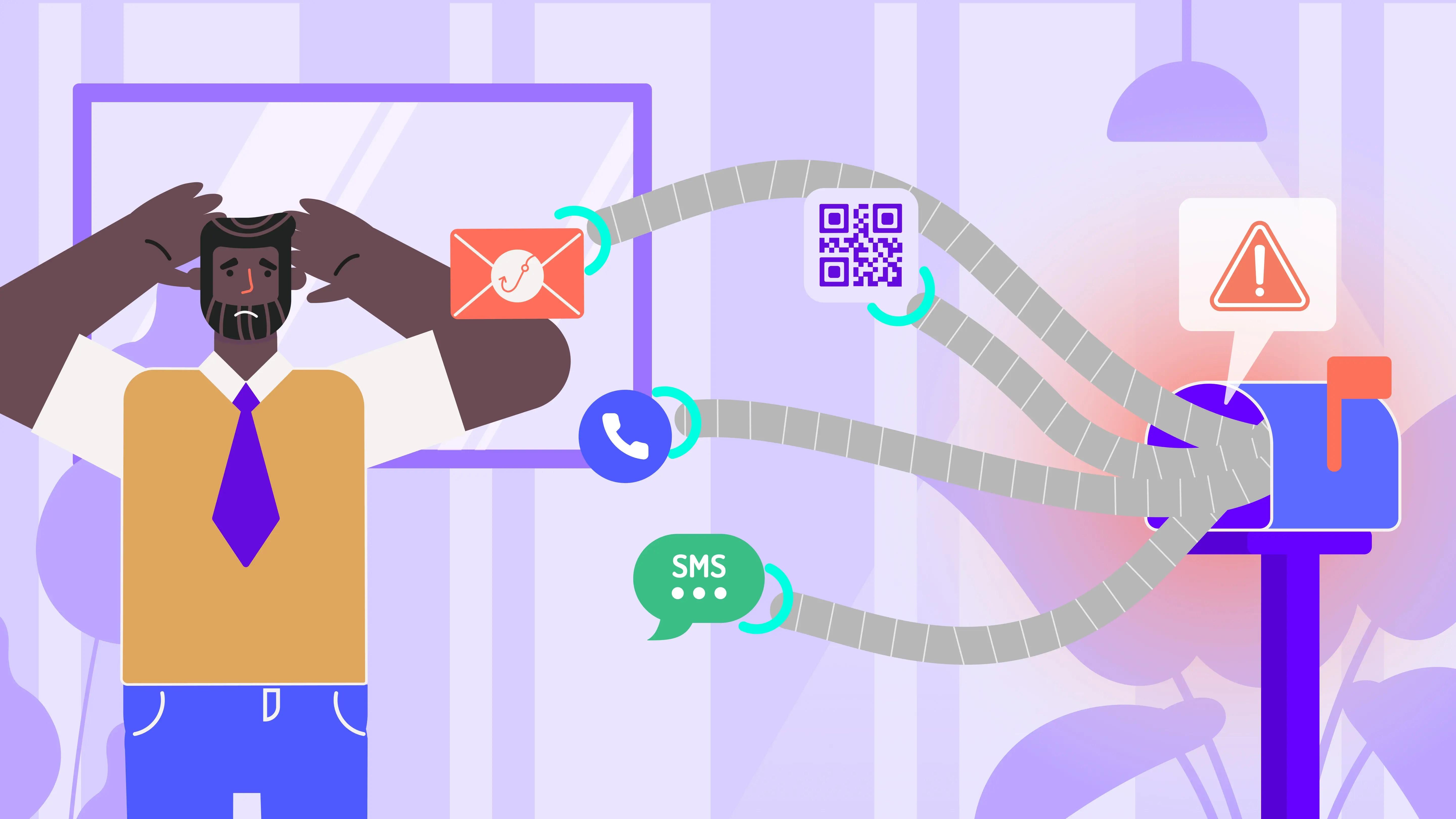
Phishing, where attackers masquerade as trustworthy entities to trick users into divulging sensitive information, remains at the heart of these state-sponsored campaigns. These sophisticated tactics often include emails that appear to come from known contacts or reputable organizations, laden with malicious links or attachments designed to harvest credentials or deploy malware. These state-sponsored phishing attacks are particularly dangerous for businesses because they specifically target high-value individuals, making it critical to recognize and counteract these sophisticated strategies.
Common Phishing Techniques Used by State-Sponsored Attackers
- Spear Phishing: Highly targeted attacks where state-backed attackers thoroughly research their victims to create convincing emails that mimic legitimate sources.
- Credential Harvesting: Attackers direct users to fake login pages designed to steal usernames and passwords, allowing access to critical systems and data.
- Malware Delivery: Phishing emails often contain links or attachments that download malware onto the victim's device. This malware can monitor activities, steal data, or provide remote access to attackers.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Attackers compromise a legitimate business email account and use it to send phishing emails to unsuspecting colleagues or partners, making the attack harder to detect and contain.
In fact, according to the Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), 31% of all social engineering incidents involved phishing, while the median time for users to fall victim to a phishing email is less than 60 seconds. This highlights the critical need to detect and respond to these state-sponsored phishing attacks with speed and precision.
The Implications of State-Sponsored Phishing for Businesses
The implications of widespread state-sponsored phishing attacks are extensive. For businesses, falling victim to these attacks can lead to a range of severe consequences:
- Data Exfiltration: Once inside a corporate network, attackers can exfiltrate sensitive data, including intellectual property, financial records, and personal information of employees and customers.
- Operational Disruption: Attackers can disrupt business operations, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. A breach of this scale could disrupt operations for days or even weeks.
- Espionage: Given the state-sponsored nature of these attacks, there is a high likelihood of corporate espionage, where sensitive information is obtained to benefit foreign entities or national interests, potentially influencing market positions or affecting global competition.
A report by IBM’s X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2024 revealed that phishing, paired with infostealers, was one of the top attack vectors in 2023, contributing to 30% of incidents across industries such as finance, government, and manufacturing. This rise in state-sponsored phishing attacks highlights the need for businesses to stay vigilant, strengthening defenses and taking proactive measures to counteract these threats.
How to Prevent State-Sponsored Phishing Attacks and Protect Your Organization
Given the sophisticated methods employed by state-sponsored attackers, a multi-layered defense strategy is crucial. Organizations must focus on both technological defenses and human factors to reduce their risk.
Key Steps for Phishing Prevention
- Employee Training Engagement: Human error remains a weak link in cybersecurity. Regular training helps employees recognize state-sponsored phishing attempts and react appropriately. Real-world simulations provide hands-on experience in identifying suspicious emails.
- Advanced Email Filtering Systems: Deploy advanced email filters that can detect and block phishing emails before they reach users’ inboxes. Solutions utilizing machine learning and AI are particularly effective at adapting to new phishing tactics, including those from state-sponsored sources.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct frequent security audits to identify vulnerabilities within your organization’s systems. Make sure to update your security protocols based on the latest threat intelligence, especially related to state-sponsored attacks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide more than one piece of evidence to verify their identity. This step can significantly reduce the likelihood of credential theft from phishing.
- Endpoint Protection: Ensure that all endpoint devices are protected with up-to-date security software, including anti-malware programs and firewalls. This helps to detect and neutralize threats before they compromise sensitive data.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan. This plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a security breach, including how to isolate affected systems and communicate with stakeholders.
Vigilance is Key to Defending Against State-Sponsored Phishing
The rise of state-sponsored phishing attacks targeting corporate users underscores the urgent need for heightened vigilance. As attackers continue to refine their tactics, businesses must stay proactive by investing in comprehensive cybersecurity solutions, continuously educating employees, and regularly updating their defense strategies.
Phishing attacks can happen in seconds, but with the right defenses, businesses can minimize the risks from these state-sponsored phishing attacks. Stay informed, stay prepared, and ensure that your organization is equipped to face the evolving threats in the cybersecurity landscape.